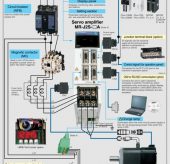
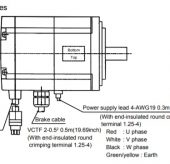
A servo is a type of motor commonly used in robotics, automation, and other applications where precise control of motion is required. Servo motors are designed to rotate to a specific angle or position, and maintain that position until commanded to move to a new position.
Servo motors typically consist of a DC motor, a gearbox, and a control circuit. The control circuit receives signals from a controller, which specifies the desired position of the motor. The control circuit then adjusts the voltage supplied to the motor in order to move the motor to the desired position, and maintains that position through feedback from sensors that detect the motor’s position.
Because servos can be controlled with a high degree of precision, they are commonly used in applications such as robotics, CNC machines, and camera stabilization systems. Servo motors come in a variety of sizes and torque ratings, and can be used in both small and large-scale applications.